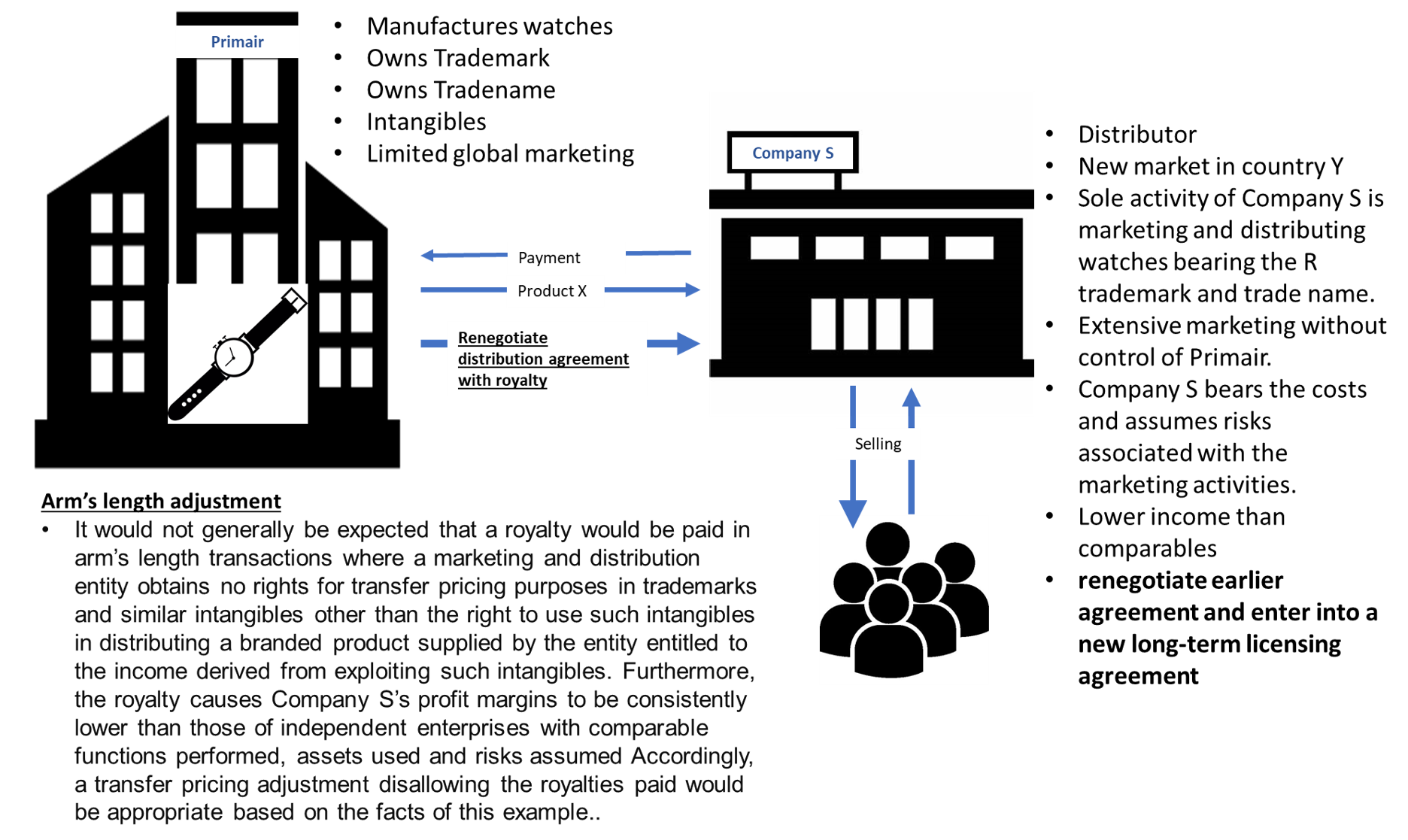
39. The facts in this example are the same as in Example 9 with the following additions:
- By the end of Year 3, the R brand is successfully established in the country Y market and Primair and Company S renegotiate their earlier agreement and enter into a new long-term licensing agreement. The new agreement, which is to commence at the beginning of Year 4, is for five years with Company S having an option for a further five years. Under this agreement, Company S agrees to pay a royalty to Primair based on the gross sales of all watches bearing the R trademark. In all other respects, the new agreement has the same terms and conditions as in the previous arrangement between the parties. There is no adjustment made to the price payable by Company S for the branded watches as a result of the introduction of the royalty.
- Company S’s sales of R brand watches in Years 4 and 5 are consistent with earlier budget forecasts. However, the introduction of the royalty from the beginning of year 4 results in Company S’s profit margins declining substantially.
40. Assume that there is no evidence that independent marketers/distributors of similar branded products have agreed to pay royalties under similar arrangements. Company S’s level of marketing expenditure and activity, from Year 4 on, is consistent with that of independent enterprises.
41. For transfer pricing purposes, it would not generally be expected that a royalty would be paid in arm’s length transactions where a marketing and distribution entity obtains no rights for transfer pricing purposes in trademarks and similar intangibles other than the right to use such intangibles in distributing a branded product supplied by the entity entitled to the income derived from exploiting such intangibles. Furthermore, the royalty causes Company S’s profit margins to be consistently lower than those of independent enterprises with comparable functions performed, assets used and risks assumed during the corresponding years of similar long-term marketing and distribution arrangements. Accordingly, a transfer pricing adjustment disallowing the royalties paid would be appropriate based on the facts of this example.